Healthcare data plays a critical role in every health service at varying scales. Doctors need to access your medical history for a reliable evaluation at a Telehealth appointment. On the other hand, wearable technology, like a Fitbit or Apple Watch, can track movement to create a constant stream of personalized medical data too. Nonetheless, in both cases, health data is critical for both of these services.
From large volumes of health data comes new opportunities to discover and deliver the best medical care. However, it’s vital to have proper data systems to get the right healthcare data where you need it and when you need it. This is one of many challenges of integrated healthcare systems.
Why is medical data important in healthcare?
When you book an appointment, your data is electronically stored. These virtual records are replacing paper records because of its ability to store more information and quickly query results. This information includes the reason for your visit, symptoms, and medical history. How does your doctor know how to use your data to give a proper diagnosis and treatment? By having the right medical data where you need it and when you need it!
From health records to wearable technology, the healthcare industry collects large amounts of data every day. To illustrate how large, the estimated amount of global healthcare data in 2020 was about 2314 exabytes (1 exabyte = 1 billion gigabytes). This mountain of data could help with everyday decisions and predictions for the future if properly managed and analyzed. This is why data is important in healthcare.

However, with medical data scattered across multiple sources such as a hospital, a walk-in clinic, and your Fitbit, how can data be used and accessed from one place? By using a robust data infrastructure for integrated medical data. A strong infrastructure can set the groundwork to collect, clean, analyze, and integrate data. Setting this groundwork can pave the path to more meaningful medical decisions. This is one of many data challenges in healthcare.
Spatial big data in healthcare
Big data, particularly spatial big data, can significantly impact healthcare. Spatial big data is big data with additional geographic components such as absolute and relative location. With almost everyone owning a mobile device, spatial big data is also convenient to collect. As spatial data has helped researchers understand COVID-19’s movement, its role in healthcare has become more evident. Beyond tracking COVID-19, spatial big data helps us understand the impact of policies implemented throughout the pandemic. While spatial big data is helpful, there are areas of concern regarding collection methods, intended usage, and data integrity.
Telehealth: What data health challenges did the COVID-19 pandemic reveal?
Many organizations worldwide were unprepared when the COVID-19 pandemic hit. The pandemic’s beginning brought in large surges of data that many healthcare systems were unsure of how to manage. As we come to the end of 2021, almost two years since the report of the first COVID-19 case, we can reflect on what data challenges arose throughout the pandemic and how health organizations, especially the Telehealth industry, can be proactive in dealing with future outbreaks.

Teleheath, accessibility and cost of health services
COVID-19 continues to affect our everyday lives by restricting our physical movement. With most countries enforcing lockdowns throughout 2020, it was challenging to access grocery stores, malls, and, most importantly, health services. With limited access to routine check-ups and medication, healthcare providers and patients struggled to give and receive treatment. This was especially true for rural communities that already lacked access to these services before the pandemic. A temporary solution to this accessibility issue was Telehealth services, which offered flexibility and lower costs for patients and physicians. As we gradually move towards a digital-first world, Telehealth services are rising in popularity, particularly for mental health and primary care. Healthcare data needs to be managed properly to support and improve these services continually.
Proper data management infrastructure
Extracting relevant information and finding connections between datasets in large volumes of raw data can be tedious and costly. It isn’t uncommon to also find data gaps when collecting raw data, and filling these gaps requires an infrastructure that can easily integrate different data sets.
While it’s easy to dismiss these data gaps, these gaps need to be filled in order to provide high-quality health data. With high-quality health data, higher-quality healthcare will follow. If hospitals and health organizations have the appropriate data systems in place to collect, clean, analyze, and integrate data, this can lead to reduced medical costs, more accurate diagnoses, and faster decision-making.
How can FME be used to integrate healthcare data?
Over the past year, the COVID-19 pandemic has proven the need to integrate spatial and healthcare data to make informed decisions within the healthcare sector.
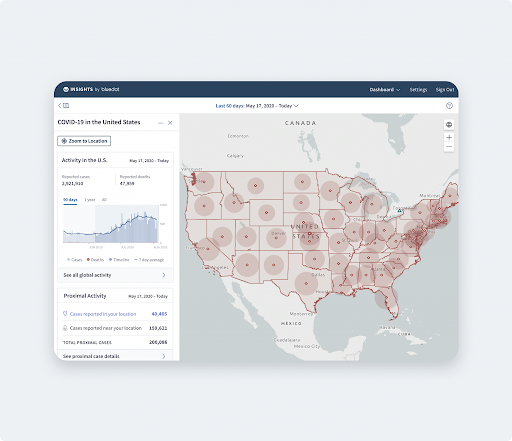
This is particularly evident when dealing with outbreaks, as spatial big data can help track and predict the movement of diseases and populations. Learn more about how FME has been used to integrate healthcare data by BlueDot:
[Customer Stories] Bluedot
[Blog Post] How BlueDot Leverages Data Integration to Predict COVID-19 Spread
[Webinar] Leveraging Data Integration to Predict COVID-19 Spread: Interview with BlueDot