Extracting Geospatial Data from PDFs: Top 3 Challenges


You’ve been given a dataset that promises to contain valuable information. It’s got maps, measurements, CAD drawings—everything you need to do a great job! Except (sad trombone sound) the data is in PDFs. PDFs! What In The Name Of Adobe are you supposed to do with that? Open 500 files and manually punch every number into a calculator? No, thanks.
From accountants to data technicians and beyond, the need to extract data from a PDF has plagued all of us at some point. Software like Adobe is great if you need to edit well-formed text and tables—but if you’ve landed here, you probably need more than that. Let’s look at how to convert a PDF into valid data that you can load into your GIS, CAD system, database, etc., for further use.
Basic PDF Conversion Workflow
1. Add a PDF Reader to your FME workspace to automatically extract data from input PDFs, including:
- maps
- rasters / images
- geometry and other vector data
- text and tables
- attribute information and coordinates
- metadata, like document info and page dimensions
2. Send the data through a combination of FME transformers — because data extraction is one thing, but the whole point is to gain insight from what’s in the PDF. This is where you can perform calculations and measurements on the data, integrate it with other sources, apply regex, and otherwise process it before exporting.
3. Add a Writer to convert your transformed data into a useful format – GIS, CAD, Excel, database, Word, business intelligence software, whatever you need.
Okay, this is all fine and dandy in theory—but extracting information from PDFs is rarely so straightforward. Let’s look at some top challenges and how to overcome them.
Tutorial: Getting Started with PDF reading in FME
Challenge 1: Scanned PDF documents are not parsable
Often, data technicians are given scanned documents that are just pages of rasters – no geometry, no parsable text. Old maps and hand-drawn plans are common culprits.
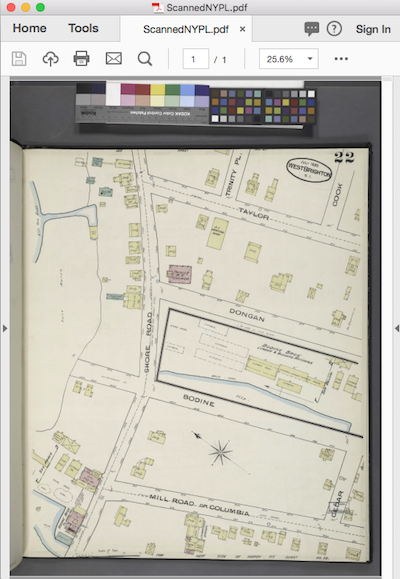
To create vector objects from a scanned image, you need feature extraction. To parse text from a file like this, you need OCR (“optical character recognition” – the automated process of extracting text from an image).
Useful FME transformers:
- TesseractCaller – calls a third-party library from within FME that performs OCR.
- RasterConvolver – performs complex raster operations, like edge detection. This helps extract geometries from ordinary images.
- RasterExpressionEvaluator – lets you perform pixel-by-pixel calculations on a raster, so can be used to extract features and do other raster operations.
- PotraceCaller – calls a third-party library to turn bitmaps into vector graphics. See also: 3 Ways to Convert Raster Images to Vector for CAD/GIS.
A Boring Project
Here’s a boring example. I mean, “the act of making a hole” boring, not “Zzzz” boring.
Sander Meijer of Sweco Netherlands gives a “Boring” talk on using FME to reclaim bore hole data stored in PDF using such goodies as the TesseractCaller and the all new PDF Reader #FMEWT Copenhagen pic.twitter.com/ASxsvWeVPM
— dale_lutz.fme (@DaleAtSafe) May 29, 2018
Challenge 2: Bulk processing
Data conversion is usually not a one-time thing. If you have a PDF to process, there’s a good chance you actually have more than one of them. Because FME workflows are repeatable, bulk processing is as easy as feeding your workspace the directory of PDFs—or setting up a schedule or trigger in FME Flow and letting the workspace run whenever new data arrives.
You could even create a self-serve web portal via FME Flow and let end users perform PDF conversions themselves.
Challenge 3: Extracted data needs to be cleaned up
Polygons are broken, lines are disconnected, text is garbled, every letter in the PDF is stored in an individual text box rather than a connected string … Help.
Once you extract data from a PDF, it likely needs a bit of repair. FME has a few transformers that can help you intelligently clean up the data.
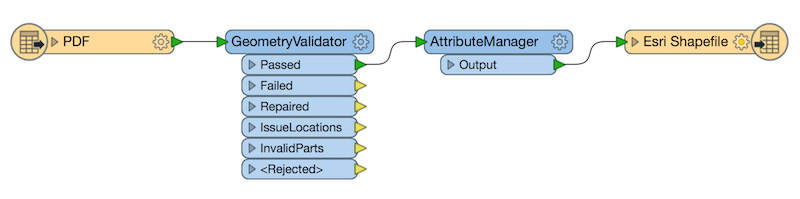
Useful FME transformers:
- GeometryValidator – to detect and repair bad geometry.
- Snapper – to snap broken lines together.
- AttributeManager – to add and update the attributes associated with a data feature.
- MapTextLabeller – to annotate the geometry with high-quality cartographic labels.
Do you need to extract data from a PDF? Please let us know what tutorials/templates you need and how we can improve FME’s PDF reading functionality.
Learn more: check out these tutorials in the FME Community.



